Blog
August 7, 2025
Drupal PHP support is inextricably linked to the fast-moving PHP support lifecycle, as Drupal is one of the leading PHP-based content management systems (CMS) for web development. However, understanding Drupal PHP requirements by version, and the time span for which Drupal supports specific PHP versions, can be confusing.
In this blog, we look at the Drupal PHP version support lifecycle, including details on the Drupal release cadence, how that cadence corresponds to the PHP release lifecycle, and variables that can alter the typical Drupal PHP version support schedule.
Table of Contents
Drupal PHP Overview: Understanding the Drupal Release Cadence
Before we can talk about how Drupal consumes PHP, it’s important to understand the typical Drupal pre-release and general availability (GA) release cadences.
In the chart below, which is an example from Drupal, you can see how the typical release and support cadence works. As noted by Drupal, the exact schedule varies, and it is typically maintained by following the Drupal core release schedule.
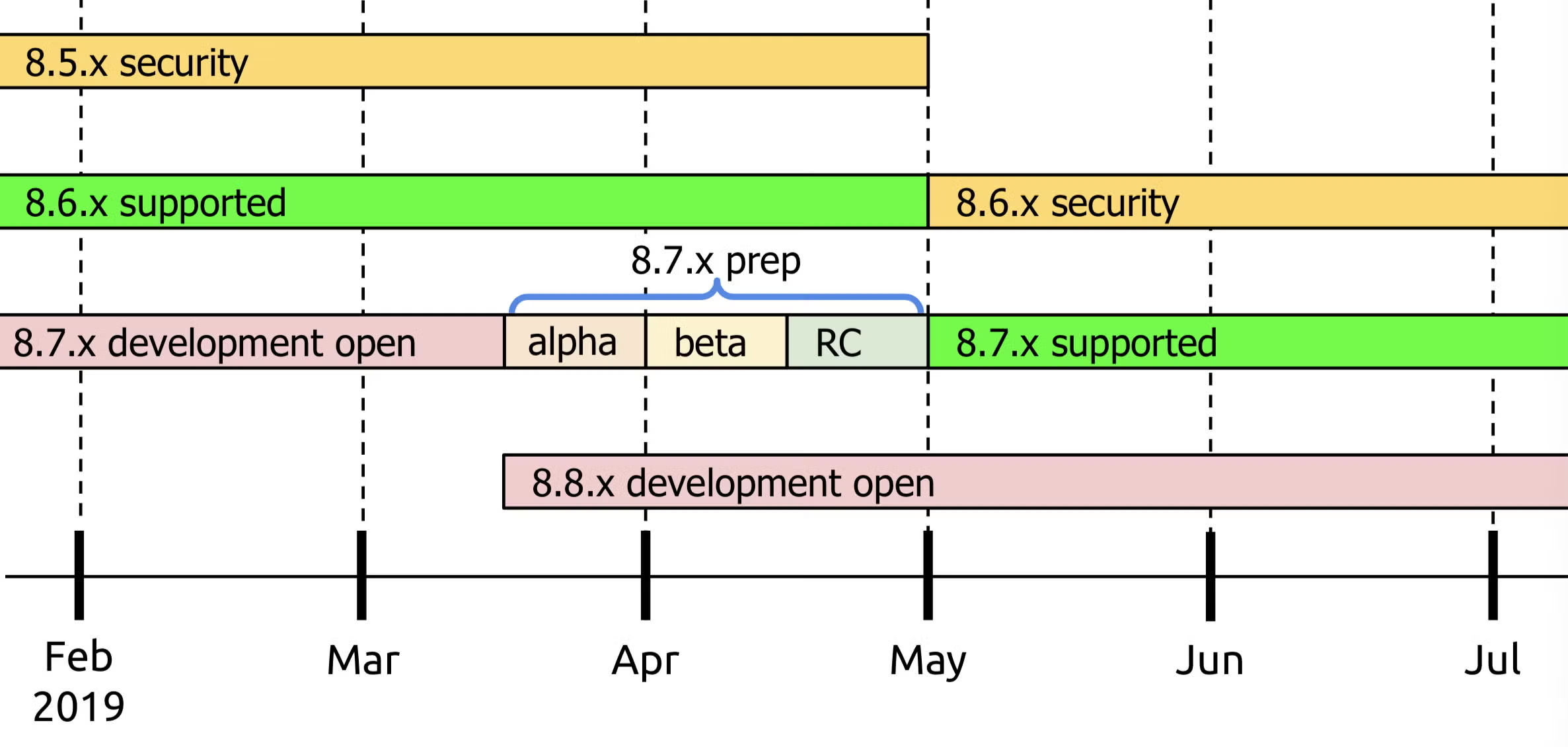
Drupal Pre-Release Stages
Before Drupal versions are released to the public, they undergo a period of behind-the-scenes development. That development period is then followed by alpha releases, beta releases, and release candidate releases before it reaches public GA.
- Alpha releases represent the least stable release category, typically containing a number of unresolved, known issues.
- Beta releases fix most issues and allow a somewhat stable platform for module and theme creators to start working toward compatibility.
- Release candidates deliver generally stable code with no remaining critical bugs.
An in-depth explanation of Drupal pre-release stages can be found in the Drupal documentation. In the table below, you can see an applied example of these release stages as they occurred for Drupal 7.
| Drupal Version | Release Date |
|---|---|
| drupal 7.x-dev | 7/2/2008 |
| drupal 7.0-alpha1 | 1/15/2010 |
| drupal 7.0-alpha2 | 2/21/2010 |
| drupal 7.0-alpha3 | 3/21/2010 |
| drupal 7.0-alpha4 | 4/26/2010 |
| drupal 7.0-alpha5 | 5/23/2010 |
| drupal 7.0-alpha6 | 7/9/2010 |
| drupal 7.0-alpha7 | 9/16/2010 |
| drupal 7.0-beta1 | 10/7/2010 |
| drupal 7.0-beta2 | 10/23/2010 |
| drupal 7.0-beta3 | 11/14/2010 |
| drupal 7.0-rc1 | 12/1/2010 |
| drupal 7.0-rc2 | 12/11/2010 |
| drupal 7.0-rc3 | 12/23/2010 |
| drupal 7.0-rc4 | 12/30/2010 |
| drupal 7.0 | 1/5/2011 |
Drupal versions fall into one of two categories: major or minor. The length of time that the pre-release cycle requires will vary depending on the type of Drupal version.
For minor Drupal versions, the post-development and pre-release phases typically last around six weeks.
Major Drupal versions can spend up to 2.5 years in development and pre-release stages, with the community cadence dictating two months in the beta release phase and one month in release candidate phases. Drupal 7, for example, spent 562 days in the development phase, 265 days in the alpha release phase, 55 days in the beta release phase, and 35 days in the release candidate phase before being reaching GA.
| Stage | Days Per Stage | Releases Per Stage |
|---|---|---|
| Dev | 562 | 1 |
| Alpha | 244 | 7 |
| Beta | 55 | 3 |
| Release Candidate | 35 | 4 |
Drupal General Availability: Major vs. Minor vs. Patches
Drupal General Availability releases occur roughly every two years — always on the even year — with minor Drupal version releases for those major versions occurring every 6 months.
After Drupal 7, which used decimal versioning, Drupal adopted semantic versioning. As an example, when this versioning approach is applied to X.Y.Z, X would represent a major version, Y would represent a minor version, and Z would represent a patch version.
Breaking down the changes for each type of release, patch versions consist of bug fixes and security fixes, minor versions can introduce new features, and major versions can introduce backwards-incompatible changes.
On-Demand Webinar
Are CMS Ecosystems Keeping Pace With PHP?
The PHP experts dive in on the state of PHP support within content management systems, including discussions on how Drupal PHP ingestion occurs, the current state of Drupal PHP support, and more.
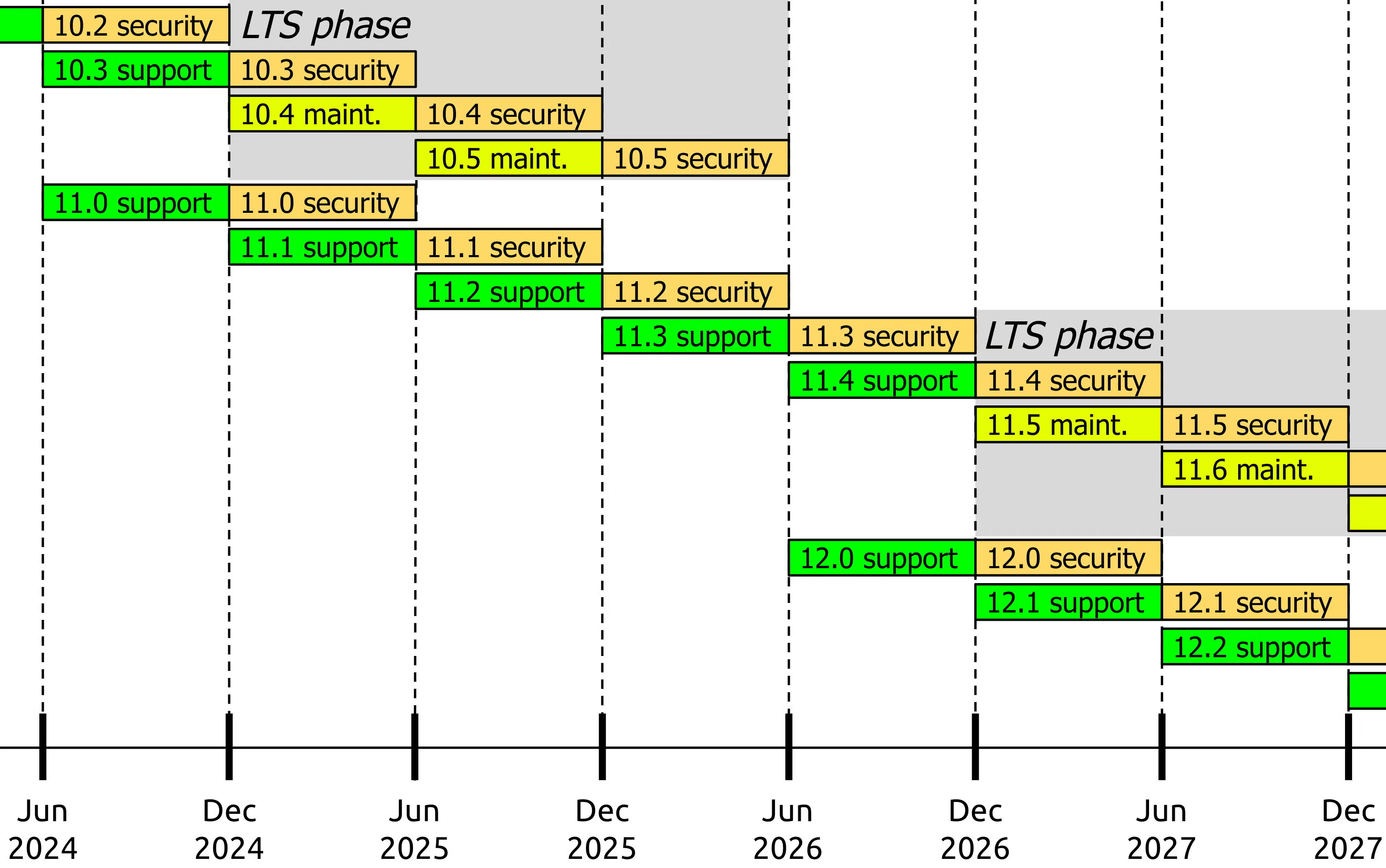
Drupal Community Support Timeline
Like many open source projects, the Drupal community provides support (including new features, patches, and bug fixes) for Drupal versions along a specified timeline. Beginning with Drupal 10, major versions are supported for at least four years and receive active support for two years after release, and maintenance and security support for two years after that.
Minor Drupal versions are released every six months and receive one year of active community support (six months of bug fixes and security patches, six months of security patches only).
Beyond major and minor Drupal versions, there is also the matter of long-term support, or LTS, versions. The terminal minor version for a major version (e.g. Drupal 9.5.0) is designed as a LTS version and receives security patches for an additional amount of time determined by the community.
The chart below, for example, shows a sample release schedule for the 10.x, 11.x, and 12.x Drupal releases. 10.3, a minor version, is supported for a total of one year, with a six-month phase of active community support, and six months of security support.
Back to top
Drupal PHP: What's the Connection?
Drupal uses and interacts with PHP in several fundamental ways. Namely, the Drupal core is written in PHP. Beyond the Drupal core, PHP is also used in Drupal themes, modules, templates, and in interactions between Drupal and database systems like MySQL or PostgreSQL.
Drupal provides a list of common ways in which Drupal interacts with PHP versions. These include database extensions, the XML extension, image library, OpenSSL, JSON, cURL, and Mbstring.
It's also worth noting that the recommended Drupal PHP version can be impacted by its own underlying dependencies. Components from Symfony, for example, are used within the Drupal core library. This means that if Symfony requires a specific version of PHP, the Drupal version that incorporates that specific Symfony version will also need to require that specific PHP version. An example of that is found with Drupal 10, which uses Symfony 6. Since Symfony 6 requires at least PHP 8.1, Drupal 10 also requires PHP 8.1.
mittwald Managed Hosting Customers Stay Secure With Zend
mittwald, a global leader in web hosting, partnered with Zend to deliver value, security, and peace of mind to their customers, including those running Drupal PHP apps.
Compatible vs. Recommended Drupal PHP Versions
At a high level, Drupal tries to align PHP version support to the PHP community support lifecycle, cycling in new recommended versions as they’re made compatible within the Drupal ecosystem and removing recommended status for PHP versions that have reached community support end of life.
With this in mind, Drupal PHP version support can be broken down into two categories: Compatible and Recommended.
Compatible Drupal PHP Versions
Many pieces of software, including Drupal, have minimum operating requirements. For Drupal, this includes a minimum PHP version. Compatible versions range from the minimum compatible PHP version to the latest supported PHP version.
By using a compatible PHP version, you ensure that Drupal core features will work as intended. However, a compatible version will not ensure that you receive the latest improvements, optimizations, or security updates found in newer PHP versions.
Recommended Drupal PHP Versions
Recommended Drupal PHP versions are versions endorsed by the Drupal community. They are recommended primarily because of their status as community-supported PHP versions, but also because they offer the best performance, security, and compatibility with Drupal themes, modules, and extensions.
Once a PHP version is no longer community supported, they typically are no longer listed as recommended versions for Drupal.
Example: Drupal 10 Compatible vs. Recommended Versions
According to the Drupal PHP requirements and further detailed in the next section, Drupal 10 requires at least PHP 8.1 in order to be deployed. However, while PHP 8.1.0 will meet the minimum requirements, the recommended PHP version is PHP 8.1.6.
Back to topDrupal PHP Requirements: PHP Support by Drupal Version
With both the Drupal and PHP communities setting an aggressive release pace, keeping up with the individual requirements of specific Drupal versions is critical for deploying successful Drupal PHP web apps. In this section, we break down supported Drupal and PHP versions to ensure your critical apps remain secure, supported, and performant.
At-A-Glance: Drupal PHP Requirements
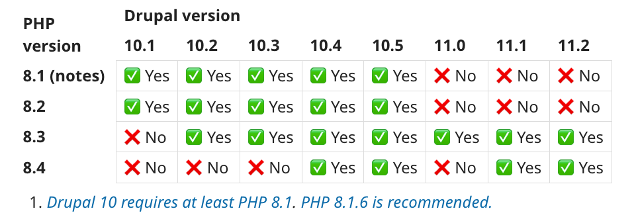
Drupal 7 PHP Requirements
As of January 5, 2025, Drupal 7 is no longer supported and does not receive security updates or compatibility extensions, despite having been extended previously. If you are still deploying Drupal 7 in PHP applications, you must make a migration plan now.
Before reaching end of life, Drupal 7.92 and subsequent 7.X versions recommended use of PHP 8.1 and 8.2, with PHP 8.3 supported and recommended as of Drupal 7.94. Previously, Drupal 7.x versions supported PHP 5.6 and up, with PHP 7.2.x and up being the recommended versions.
Learn More About Drupal 7 PHP Version Requirements
Drupal 8 PHP Version Requirements
Drupal 8 versions reached end of life and support in November, 2021.
As Drupal 8 was dependent on Symfony 3, and Symfony 3 EOL occurred in early November, 2021, Drupal 8 can no longer be supported. An LTS version, Drupal 8.9, was released alongside Drupal 9 that same year. However, no new features will be added to Drupal 8, and no new minor versions will be made available.
Before reaching EOL, Drupal 8 required at least PHP 5.5, but it expanded to support up to PHP 7.4. As it is now EOL and unsupported, Drupal 8 is not recommended for use. Teams should upgrade as soon as possible to a supported Drupal version.
Drupal 9 PHP Version Requirements
Drupal 9.0.0 was supported through November 1, 2023, when it reached EOL alongside Symfony 4.
Before this EOL event, Drupal 9.0.0 required at least PHP 7.4 and supported up to PHP 8.1. As it then reached EOL, Drupal 9 will not support versions beyond PHP 8.1. To take advantage of the latest PHP features, your team will need to update your application to Drupal 10 or newer.
Learn More About Drupal 9 Support
Drupal 10 PHP Version Requirements
Drupal 10 reached GA in December 2022, and it is scheduled to reach EOL upon the release of Drupal 12 in mid to late 2026.
Drupal 10 requires a minimum of PHP 8.1 to run, and it is compatible with PHP 8.2 and 8.3, which are recommended for better application performance and security.
Learn More About the Drupal 10 Release Cycle
Drupal 11 PHP Version Requirements
Drupal 11 released in August 2024. Active support will continue until approximately June 2026, when Drupal 12 is released. It will then enter maintenance-only mode until June 2027, when it will reach EOL.
Drupal 11 requires a minimum of PHP 8.3, with Drupal 11.1.0 and 11.2.0 recommending use of PHP 8.4. This makes Drupal 11 the first Drupal core version to drop support for older PHP versions, such as 8.1 or 8.2. This aligns with Drupal’s shift to match modern PHP standards, ensuring compatibility with the latest PHP performance and security improvements.
Looking Ahead to Drupal 12 PHP Requirements
Drupal 12 is currently in development, with GA anticipated in 2026.
As Drupal 12 is still in development, it is unclear what the exact PHP requirements will be. However, as Drupal versions now default to the latest stable PHP release available, it is anticipated that Drupal 12 will recommend users deploy PHP 8.5, which is scheduled to release in November, 2025.
Learn More About Getting Ready for Drupal 12
Back to topKeeping Pace With Drupal PHP Requirements
Depending on the size or age of your application, managing the PHP support lifecycle within your Drupal-based application can be complex and time-consuming.
In order to stay secure and avoid incompatibilities long term, teams will need to regularly update the Drupal core, as well as manage PHP version compatibility for all themes, modules, and extensions used within the Drupal PHP application.
Drupal PHP Upgrades and Migrations
The most common way to keep up with PHP version requirements is to migrate or upgrade to the latest versions of Drupal, along with the dependencies used within your application. That said, PHP upgrades and migrations — or Drupal version upgrades and migrations — might not always be possible without substantial changes to your dependencies, which makes selecting well-used and well-supported themes and modules even more important.
One factor in Drupal’s popularity is its high customization capabilities. This means that many enterprise Drupal sites will have substantially modified code. When upgrading or migrating, ensuring these customizations will work with both the new Drupal version and the new PHP version can add significant complexity.
As a rule of thumb, the more dependencies you have, and the more customizations you have applied to your Drupal app, the further in advance you should be planning, testing, and executing your PHP upgrades or migrations.
Long-Term Support for EOL Drupal and PHP Versions
In cases where you don’t have bandwidth to perform PHP upgrades as frequently as the PHP support lifecycle dictates, or where you would like to prioritize other development initiatives, obtaining long-term support via a third party, such as Zend, is a good option to consider.
With Zend PHP long-term support, you can extend the PHP lifecycle for your application (including the lifecycle for dependencies that ingest and interact with PHP) by a minimum of two years beyond the PHP community support lifecycle.
Back to topFinal Thoughts
For many businesses, keeping Drupal versions updated and aligned with community supported PHP shouldn’t be a major issue. However, for enterprise organizations that manage or host their own Drupal applications, keeping up with Drupal and PHP upgrades can pose a significant challenge – one that can ultimately divert time away from other critical development initiatives. Drupal aside, teams managing enterprise web applications will need to ensure that the PHP they ingest is kept up to date across their entire web infrastructure stack.
Luckily, there are options for teams who want to keep their Drupal applications protected against CVEs and compatibility issues – including migration services and PHP long-term support from Zend.
Need Help Keeping Your Drupal PHP Apps Secure and Supported?
Zend can help. With expert migration services and a full suite of comprehensive PHP support, we can keep your Drupal PHP application secure, optimized, and ready for the next release.
Additional Resources
- Solution - Symfony Migration Support
- Resource Collection - PHP Versions: Performance, Security, and Feature Comparisons
- Guide - How to Develop Web Applications with PHP
- White Paper - Planning Your Next PHP Migration
- White Paper - The Costs of Building PHP In House
- White Paper - The Hidden Costs of PHP Upgrades
- Blog - The State of WordPress PHP Support
- Blog - How to Assess and Prevent PHP Vulnerabilities
- Blog - How to Configure nginx for Drupal 10 and PHP-FPM
- Blog - CMS or Framework: What's Best for Your PHP Application?
