Blog
January 15, 2026
Is PHP still relevant in 2026? Short answer: Yes, and it shows no signs of going anywhere.
For over three decades and continuing into 2026, PHP has been the silent workhorse of the modern web. In fact, many users are interacting with PHP every day without realizing it. Major platforms like WordPress and Drupal, which dominate the content management space, are built on PHP, and popular frameworks like Laravel and Symfony are built using the language. From personal blogs to complex enterprise systems, PHP’s usage remains widespread, even as newer technologies emerge and grow.
In this blog, I explore the evolution of PHP and its continuing relevancy. I take a look at the modern ecosystem, discuss the benefits of working with PHP, and go through a few key use cases. I also examine other popular backend technologies and their place alongside PHP in the current landscape.
The Evolution of PHP
PHP was first created in 1994 by Rasmus Lerdorf. It began as a simple set of Common Gateway Interface (CGI) binaries and was not intended to be a programming language. Instead, it solved a very specific problem: creating dynamic web pages easily.
In the 30+ years since, PHP has evolved from a templating engine into a dominant scripting language. In 2005, the release of PHP 5 introduced proper object-oriented programming (OOP) and laid the groundwork for modern frameworks. But, while PHP 5 had a number of significant changes — notably, the addition of namespaces in 5.3 and the by-default inclusion of an OpCache in 5.5 — the true turning point came with the release of PHP 7 in 2015.
PHP 7.X versions dramatically reduced memory consumption and increased performance, often doubling the speed and halving the memory consumption of applications compared to PHP 5.6. It also introduced some new features around type safety, which the language continues to iterate over today.
By the time PHP 8.0 released in 2020, the language had matured into a powerhouse. The introduction of the Just-In-Time (JIT) compiler marked a major milestone, allowing PHP to execute code that was previously computationally expensive with greater efficiency. When we add in enumerations with PHP 8.1, quality of life improvements with PHP 8.2 and PHP 8.3, property hooks in PHP 8.4, the pipe operator in PHP 8.5, and many other updates and new features – it becomes easy to see why PHP continues to be a major player in the 2026 web landscape.
Learn More About the Evolution of PHP
Back to topModern PHP and the Current Ecosystem
While it is true that PHP usage has declined slightly in recent years, it remains the most popular choice for server-side languages by a wide margin. Other technologies and languages include Ruby and Ruby on Rails, Node.js and JavaScript, Java, Python, and others. You can check out a quick comparison below.
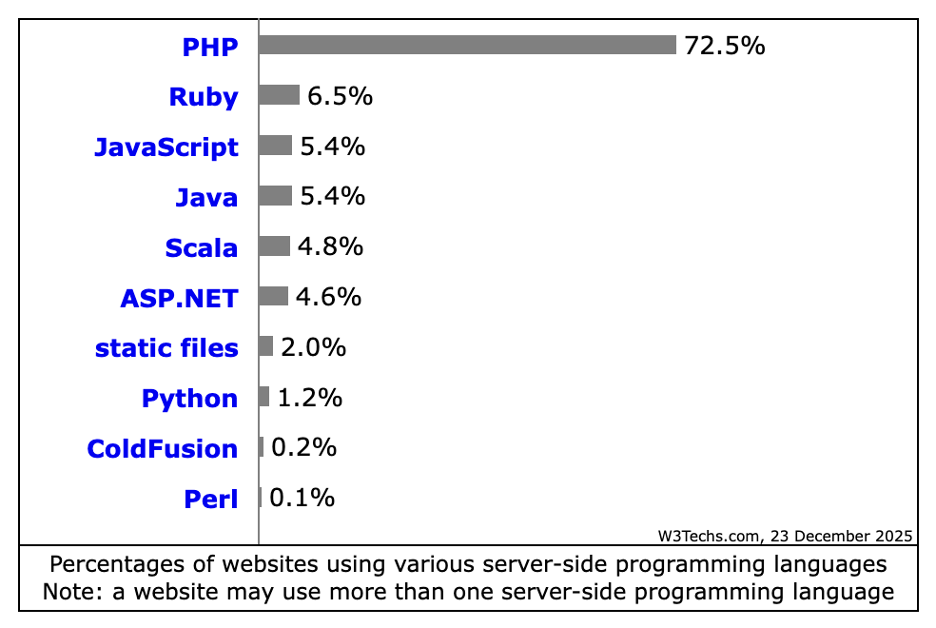
For many developers, PHP’s widespread use will come as little surprise. It thrives because it has adapted to modern development practices – I go into more detail below.
Performance and Security Improvements
With the advancements in PHP 8.X, performance is rarely a bottleneck for PHP web applications. The JIT compiler and improvements to the Zend Engine ensure that PHP handles high-concurrency requests efficiently.
Security has also become a primary focus. The core PHP team releases regular updates to patch vulnerabilities. Modern frameworks come with built-in protection against common attack vectors like SQL injection, Cross-Site Scripting (XSS), and Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF). When managed correctly, a PHP application is as secure as any banking-grade software written in Java or Go.
Frameworks and Tools
PHP’s "spaghetti code" reputation of the past has been dismantled by a sophisticated ecosystem of frameworks and tools. While this list is by no means exhaustive, here are a few examples:
- Laravel, the leading PHP framework, brings elegant syntax and developer friendly tools. It simplifies rapid application development (RAD) without sacrificing code quality. Learn more about Laravel Framework.
- Symfony is a framework and set of reusable PHP components. It is used in many large-scale applications and frameworks (including Drupal and Laravel), and it enforces strict coding standards and best practices. Learn more about Symfony Framework.
- Composer is a dependency manager that allows developers to easily manage libraries and packages, similar to npm in Node.js or pip in Python. Learn more about using Composer for PHP dependency management.
Cloud-Native and Containerized Environments
PHP has proven itself highly adaptable to modern cloud-native and containerized deployment models. The language easily integrates with containerization tools like Docker, empowering teams to build lightweight, isolated PHP environments that are consistent across development, testing, and production stages.
Orchestration platforms such as Kubernetes seamlessly manage PHP containers. PHP’s compatibility with popular cloud service providers allows organizations to leverage cost-effective, scalable deployment strategies.
Back to topWhen to Use PHP: Key Use Cases
PHP has always been a strong choice for a wide range of web app development projects, and that continues to be true in 2026. Whether you’re using a content management system (CMS), looking to speed time to market, or building enterprise-scale web applications or APIs, PHP offers unique advantages compared to other server-side and backend technologies.
Learn More About Developing Web Applications with PHP
Content-Heavy CMS Applications
If your project involves heavy content management, PHP is the undisputed champion. Platforms like WordPress, Joomla, and Drupal have matured into enterprise-grade Content Management Frameworks. Building a custom CMS or a content-heavy portal in another language often involves reinventing the wheel, as PHP provides a massive head start with its rich library of themes, plugins, and existing CMS architectures.
Rapid Prototyping and MVPs
Speed to market is a critical metric for most organizations, and PHP allows for incredibly fast development cycles. Its "shared-nothing" architecture simplifies deployment, and the vast availability of libraries means developers rarely start from scratch. For building a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) to test a market hypothesis, PHP offers a balance of development speed and future scalability that is hard to beat.
Enterprise Web Applications
PHP is a strong choice for enterprise web applications that demand reliability, security, and performance at scale. With its active development community addressing vulnerabilities and a broad ecosystem for seamless integration with ERP and CRM systems, PHP excels as a reliable backbone for mission-critical applications in finance, healthcare, e-commerce, and other strictly regulated industries.
Back to topPHP Alternatives: Evaluating Popular Backend Technologies
Despite the continuing relevancy and many use cases of PHP, it is not the best choice for every application. In today’s rapidly changing tech landscape, different projects will come with unique requirements, and other technologies may provide better advantages. Additionally, for applications built with a microservices architecture, you may find yourself using multiple server-side languages within a single system. It's important to know which is the best fit for your specific need.
Let’s take a look at a few PHP alternatives, and explore when teams may be better served using one over PHP.
Modern PHP Versions vs. EOL PHP Versions
Before I get into PHP alternatives, it’s important to look at why a developer team may feel that PHP is no longer relevant. Often, it is because they are deploying EOL PHP versions that are no longer supported by the community. As these versions lack crucial security patches, performance optimizations, and modern language features, it’s no wonder that these teams wonder if PHP is still relevant and view the language as “falling short."
According to the 2026 State of Open Source Survey, full report to be published in early 2026, nearly 25% of surveyed teams are currently deploying PHP 7.3 (EOL in 2021) or earlier in critical applications.
By judging PHP based on experiences with legacy codebases, you are missing the reality of modern PHP. Current PHP versions deliver faster execution, stronger type safety, and built-in security enhancements that older versions simply can’t match. Staying current reduces vulnerability exposure, improves developer productivity, and ensures compatibility with modern frameworks and tooling.
Plan Your PHP Upgrade
Despite the many benefits, PHP version upgrades can be challenging, particularly for complex applications deploying PHP 7.4 or earlier. Zend Migration and Modernization services help you save time, increase performance, and minimize risk.
PHP vs. Python
Python has carved out a niche as the premier language for data science, machine learning (ML), and artificial intelligence (AI). If your web application relies heavily on real-time data processing, predictive analytics, or ML models, Python is likely the better choice. Its ecosystem (including Pandas, TensorFlow, and NumPy) is unmatched in this arena.
While Python frameworks like Django and Flask are excellent for web development, they do not inherently outperform PHP in standard web serving tasks. The switch to Python from PHP is usually driven by the need to integrate closely with data science workflows.
Learn More About PHP vs. Python
When to Use PHP vs. Python
| Scenario | Best Choice | Why |
|---|---|---|
| Content-heavy websites or CMS | PHP | Powers WordPress and Drupal for fast deployment. |
| E‑commerce and typical CRUD web apps | PHP | Optimized for common web tasks with strong frameworks. |
| Small to mid-sized sites with rapid launch needs | PHP | Easy to learn and quick to implement. |
| Data science, ML, and analytics workloads | Python | Rich libraries for data and machine learning. |
| API services requiring async/concurrency | Python | Excellent support for asynchronous processing. |
| Automation, scripting, and DevOps tooling | Python | Widely used for automation and infrastructure tasks. |
PHP vs. Java
For massive, complex enterprise-grade systems, Java remains a popular PHP alternative. Its strict typing, multi-threading capabilities, and vast ecosystem of enterprise tools make it a favorite in the financial and insurance sectors. Java is often chosen for backend systems that require extreme scalability and strict architectural governance.
However, Java development is typically slower and more resource-intensive than PHP development. PHP also requires less infrastructure and fewer specialized resources, leading to lower cost of ownership.
When to Use PHP vs. Java
| Scenario | Best Choice | Why |
|---|---|---|
| Content-heavy websites or CMS | PHP | Powers major platforms like WordPress and Drupal for fast deployment. |
| Small to mid-sized web applications | PHP | Quick setup and cost-effective for businesses needing flexibility. |
| Projects with tight timelines | PHP | Easier to learn and faster to implement for rapid delivery. |
| Large-scale enterprise systems | Tie | Both Java and PHP provide secure and highly scalable for mission-critical workloads. |
| Applications requiring strict compliance | Tie | Both Java and PHP are mature frameworks that ensure reliability and security. |
| Multi-threaded, high-performance apps | Java | Optimized for complex, resource-intensive processes. |
PHP vs. Node.js (JavaScript)
In recent years, Node.js has grown in popularity for building modern web apps. This is thanks to its event-driven, non-blocking architecture and use of JavaScript across the stack. In 2026, it can be the stronger choice for real-time applications demanding chat, streaming, and APIs that demand high concurrency.
That being said, it isn’t the right language for all applications, with PHP remaining the better choice for traditional web development and content-heavy sites. Additionally, PHP remains easier to deploy than a typical Node.js application, making it easier for developers to setup environments and DevOps to deploy to production. Still, Node.js offers many advantages for web teams due to its ability to handle thousands of simultaneous connections.
Learn More About PHP vs. Node.js
When to Use PHP vs. Node.js (JavaScript)
| Scenario | Best Choice | Why |
|---|---|---|
| Large-scale enterprise applications | PHP | Proven stability, scalability, and broad ecosystem support. |
| Content-heavy websites or CMS | PHP | Powers major platforms like WordPress and Drupal. |
| Long-term maintenance and support | PHP | Massive community and frequent updates ensure reliability. |
| Microservices and API-driven apps | Tie | Both Node.js and PHP are lightweight and ideal for distributed systems. |
| Real-time applications (chat, streaming) | Node.js | Event-driven architecture handles high concurrency efficiently. |
| Projects requiring full-stack JavaScript | Node.js | Enables using one language across front-end and back-end. |
PHP vs. Ruby on Rails
Ruby on Rails is known for its elegant syntax and convention-over-configuration approach, making it ideal for rapid development and startups. In 2026, Rails still appeals to teams prioritizing speed and simplicity, but its adoption has slowed, and it's less common in large-scale enterprise projects.
This declining market share and limited scalability options make Ruby on Rails less suited for enterprise-level projects compared to PHP, which offers broader support and modernization for long-term growth.
Learn More About PHP vs. Ruby on Rails
When to Use PHP vs. Ruby on Rails
| Scenario | Best Choice | Why |
|---|---|---|
| Large-scale enterprise applications | PHP | Offers better scalability and a broader ecosystem for complex projects. |
| Applications with heavy CMS needs | PHP | Powers major CMS platforms like WordPress and Drupal. |
| Long-term maintenance and support | PHP | Massive community and frequent updates ensure stability. |
| Projects requiring quick iteration | Ruby on Rails | Excels at fast changes and clean architecture. |
| Rapid prototyping or MVP development | It Depends | Rails’ convention-over-configuration speeds up development. However, a number of PHP frameworks offer similar convention-over-configuration paradigms. |
| Startup-focused web apps | It Depends | Both Ruby and PHP are ideal for small teams and rapid deployment. Notably, PHP offers easier and cheaper deployment, and modern frameworks offer similarly clean architecture and adaptability. |
The Power of Perforce
Unbeatable Expertise for Your Open Source Stack
For applications that use a PHP alternative, Perforce OpenLogic can keep your entire open source tech stack secure, performant, and compliant. OpenLogic provides support for 400+ open source technologies, including Java, Python, Node.js, and more.
Final Thoughts
PHP has come a long way since its humble days as a "personal home page" template engine. The Zend Engine powering it is one of the fastest, if not the fastest, interpreters out there, and it provides a wealth of language features that are often only associated with enterprise-grade languages.
At its heart, though, PHP is still a language that is easy to learn, with a runtime that is easy to deploy, making it a great choice for companies trying to save money or quickly prototype an application. Its rich object-oriented features and type system provide a foundation for maintainability. Add in a top-notch, extensive ecosystem with first-class QA tooling, libraries for anything under the sun, comprehensive frameworks and fantastic out-of-the-box applications such as WordPress, Magento, and Drupal, and it's not difficult to understand why PHP dominates the web ecosystem.
Mission-Critical PHP Made Possible
Zend keeps PHP applications secure, performant, and backed by industry-leading expertise. For nearly 20 years, we have been the go-to choice for global Fortune 100 companies. Check out what our fully supported runtimes and PHP services can do for your business.
Additional Resources
- About Perforce Zend
- On-Demand Webinar - How to Build a PHP Security Roadmap
- On-Demand Webinar - PHP 8.5: What's New, What's Changed, What's Next
- Blog - Choosing the Right PHP Stack
- Blog - What's the Best PHP Framework for Web Development?
- Blog - PHP Hardening: Strategies to Meet Compliance Requirements
