Blog
August 8, 2025
Scaling PHP Applications: Strategies for Meeting New Demand
PHP Development,
Performance
Scaling PHP applications is the process of expanding capacity to handle increased load and user demand. Although it is critical for the longevity and success of PHP apps, it can also be complex and impacted by multiple factors, such as sudden spikes in user traffic, more extensive data processing needs, or even the integration of new features. A non-scalable application can become a bottleneck, hindering growth and potentially causing financial losses.
In this blog, I take a deep dive into scaling PHP. I examine common challenges and barriers your team may experience, and then outline strategies and tactics to successfully scale your mission-critical PHP applications.
Table of Contents
- What Makes Scaling PHP Difficult?
- How to Scale PHP
- PHP Scaling Tactic 1: Choose the Right Hosting Environment
- PHP Scaling Tactic 2: Prioritize Efficient Code and Use Up-to-Date PHP
- PHP Scaling Tactic 3: Utilize Horizontal Scaling
- PHP Scaling Tactic 4: Implement PHP Caching
- PHP Scaling Tactic 5: Establish a Proactive PHP Monitoring and Analysis Strategy
- Final Thoughts
What Makes Scaling PHP Difficult?
Is PHP scalable?
Yes, but it can be difficult, as scaling PHP web applications involves increasing their capacity to handle growing user demand and traffic while maintaining performance and reliability. This process ensures that applications can seamlessly adapt to increased workloads without compromising speed or functionality.
Scaling can be achieved through various strategies, including vertical scaling, horizontal scaling, and optimizing application architecture and infrastructure. But, before we reach those topics, it is important to first understand the common roadblocks that can make scaling PHP a challenge for your team.
Performance Bottlenecks and Scaling PHP
Application performance is the precursor of PHP scalability. If an application performs poorly under normal load, it will be unable to handle increased traffic or user load without significant degradation in performance, making it effectively unscalable. This makes performance bottlenecks a serious complication when it comes to scaling PHP.
Bottlenecks can occur in any project methodology as they all involve some form of sequence or progression. Usually performance slows down because of limited capacity or resources, restricting the system’s ability to operate at full capacity.
In PHP projects, the most common categories of performance issues can be summarized as follow (in order of importance):
- Database Bottleneck — Slow responses from databases occur due to bad query design, locked tables, or heavy traffic. The functions that contain real-time information, like dashboards or searching capabilities, take the biggest hit.
- Software Bottleneck — Problems in application code, configuration parameters, or how the application software accesses the system resources belong to this category. Poor coding, even with sufficient hardware, can constrain performance.
- Disk Bottleneck — Low read and write speeds restrict the system’s ability to retrieve or save data. This normally impacts operations such as file downloads, uploads, and backups, particularly in programs that work with large data sets.
- Network Bottleneck — Delays, timeouts, or lost connections occur when network bandwidth is inadequate for the size of data being transferred. This is common in high-use environments or sub-optimal network architectures.
Other kinds of performance bottlenecks that can impact scaling PHP include memory bottlenecks, CPU bottlenecks, and thread or concurrency bottlenecks.
Optimize Performance With Zend Black Belt Services
Make the most of your resources with flexible Zend Black Belt Services. Using monthly service hours, combined with our unparalleled ZendHQ observability tools, our team can investigate bottlenecks, identify performance issues, and make sure you get the most out of your hardware.
How Monolithic Architectures Impact PHP Scalability
Monolithic PHP-based architectures have been the traditional choice for building software applications for many years. In a monolithic architecture, such as in many PHP application servers, all the components of an application are tightly integrated into a single codebase, making it easier to develop and deploy. However, as applications grow in complexity and user demand increases, monolithic architectures often face scalability challenges, particularly for scaling PHP.
In monolithic architectures, the codebase tends to grow over time as more features and functionality are added to the application. As the codebase grows, it becomes harder to isolate and scale individual components independently. This lack of modularity can hinder the ability to allocate resources efficiently to handle varying levels of load on different parts of the application. Furthermore, monolithic architectures are susceptible to single points of failure, meaning that if one critical component or service within the monolith fails, it can bring down the entire system.
Learn More About Migrating PHP Monolith to Microservices Architecture
Scaling PHP via Stateful Sessions
PHP allows us to track each visitor via a unique session ID which can be used to correlate data between connections. The PHP session naturally becomes the foundation for a stateful application, enabling the recording of the important data points related to the various interactions with a specific user, and therefore allowing the system to manage incoming requests without having to start from scratch.
Stateful applications have the obvious advantage of using historical data to give users what they want, but the disadvantage of needing to use extra computing resources to do so, as well as a data storage platform to manage all factors. If not handled properly, bottlenecks can quickly be created, impacting the complexity of scaling PHP applications.
Legacy Codebases and PHP Scalability
Legacy code's scalability challenges stem from outdated technology, poor structure, and lack of proper testing, hindering performance and adaptability to new requirements. Refactoring can improve scalability drastically, with techniques like identifying seams, breaking dependencies, and writing tests.
Legacy code often relies on technologies (frameworks, libraries, proprietary code, etc.) that are no longer supported or optimal for current performance needs (modern PHP frameworks and versions support non-blocking, concurrent and async coroutines), limiting performance and scalability. Lack of proper modularization, excessive dependencies or lack of PHP dependency management, and convoluted logic can make it difficult to modify and scale the code.
On-Demand Webinar: Strategies for Modernizing Legacy Web Apps
Join Matthew Weier O’Phinney (Senior Product Manager, OpenLogic and Zend by Perforce) as he moderates a conversation on legacy web app modernization with two experts who have helped Perforce customers every step of the way.
Database Constraints When Scaling PHP
Database scalability is the backbone of modern applications, ensuring seamless performance and reliability as data demands surge. To effectively scale PHP, you must also be able to scale your database.
Data Volume Management
In addressing storage limitations, organizations encounter the need to efficiently store and retrieve vast amounts of data. Data partitioning is the most common methodology for distributing data across multiple nodes, enhancing performance by reducing the load on individual servers. The distribution though raises a different problem which is managing transactions across shards, requiring meticulous coordination and tracking.
Database Performance
Enhancing database performance involves optimizing queries to streamline data retrieval processes. Query optimization techniques focus on refining search algorithms and indexing methods to expedite data access. Less CPU, memory, and network burden are key in being able to manage the highest number of concurrent queries.
High Availability and Reliability
Maintaining high availability and reliability is essential in database scalability efforts. Implementing redundancy and failover mechanisms safeguards against system failures, ensuring continuous access to critical data. Organizations must carefully balance consistency vs. availability trade-offs to guarantee uninterrupted service while upholding data integrity.
Handling Schema Changes
Adapting to evolving business requirements often necessitates schema changes within distributed databases. Organizations must carefully plan and execute alterations to database structures while ensuring minimal disruption to ongoing operations. Properly managing schema modifications involves updating metadata efficiently and validating changes across all nodes for seamless integration, always factoring in possible performance degradation that may determine scalability problems.
Back to topHow to Scale PHP
Scaling PHP allows your application to be capable of serving a growing number of users without sacrificing performance or reliability. As your user base grows, so does the strain on your servers, databases, and other infrastructure components. Scaling strategies distribute this load by increasing the power of individual components or by adding more components to share the work.
Before we get into specific tactics, however, we must understand approaches for scaling PHP. There are three primary types of web application scaling: vertical scaling, horizontal scaling, and diagonal scaling.
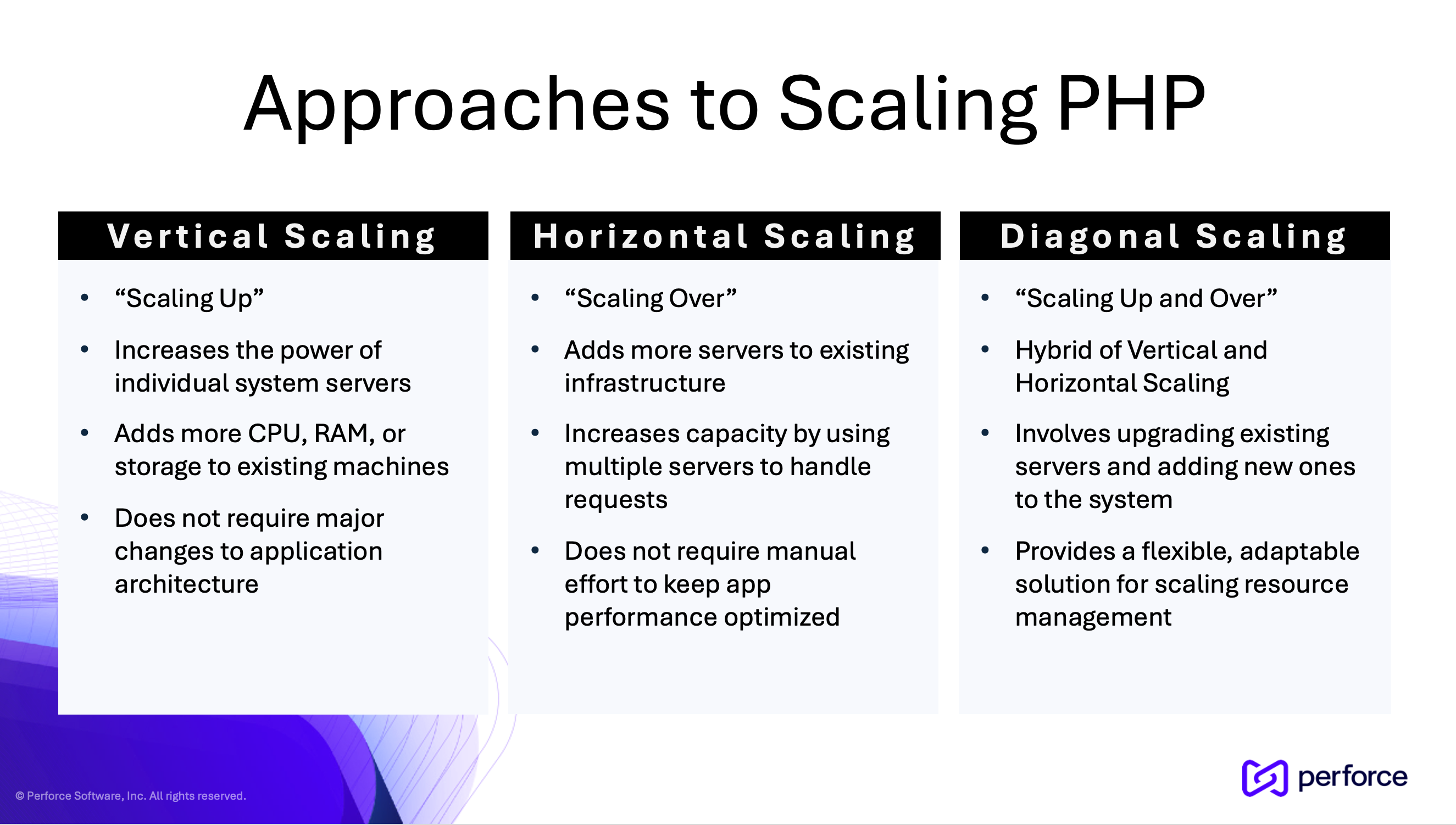
Vertical Scaling
Vertical scaling, also known as “scaling up,” involves increasing the power of individual servers in your system. This typically means adding more CPU, RAM, or storage to your existing machines. Vertical scaling is often the simplest approach because it doesn’t require major changes to your application’s architecture.
Horizontal Scaling
Horizontal scaling, or “scaling out,” involves adding more servers to your infrastructure to distribute the load. Instead of making one server more powerful, you’re increasing your capacity by using multiple servers to handle requests.
Diagonal Scaling
Diagonal scaling is a hybrid approach that combines elements of both horizontal and vertical scaling. It involves both upgrading existing servers and adding new ones to the system.
Back to topPHP Scaling Tactic 1: Choose the Right Hosting Environment
Choosing the right web hosting environment depends on your website's specific needs, including its size, traffic, and technical requirements. Shared hosting is a good starting point for beginners, while larger, high-traffic sites may require VPS, dedicated, or cloud hosting. Consider factors like performance, security, scalability, and customer support when making your decision.
Other considerations include:
- Website type and size
- Anticipated traffic volume
- Performance and speed requirements
- Security features such as SSL certificates, firewalls, and more
- Your developer team's skill set and technical expertise
PHP Scaling Tactic 2: Prioritize Efficient Code and Use Up-to-Date PHP
One of the easiest ways to ensure smooth PHP scalability is to use the latest stable version. PHP updates often include substantial performance improvements in addition to security patches and new features. As a concrete example, PHP 8 introduced the Just-In-Time (JIT) compiler, which can dynamically compile PHP code into native machine code, improving execution efficiency.
Other code optimizations should be made in ‘userland’ code, listed here in order of importance:
- Choose a performant PHP framework natively supporting highly performant architectures, possibly based on the Middleware pattern instead of the MVC one (Mezzio, Laravel, Symfony, etc.).
- Code your application to be stateless, with no session mechanism active.
- Avoid running queries in a loop and use native, optimized, SQL queries instead.
- Use asynchronous and coroutines based processing. Learn how extensions like Swoole or OpenSwoole (supported by all the above-mentioned frameworks) can drastically help increasing scalability (sometimes x10) by leveraging a modern loop-based architecture.
- Minimize file inclusions by properly using PHP’s autoloading feature to automatically load classes when needed, and always code inclusions using absolute paths.
- Use ‘generators,’ which provide an easy way to implement simple iterators without the overhead or complexity of implementing a class that implements the ‘Iterator’ interface. When using generators, PHP only keeps track of the current state of the traversal, without needing to store the whole collection that’s being traversed. Hence, execution time and memory usage during the loop execution are much lower than a regular ‘foreach’ iteration.
PHP Scaling Tactic 3: Utilize Horizontal Scaling
Horizontal scaling (scaling out), is a method of increasing system capacity by adding more machines or nodes to a network, distributing the workload across them. With the advent of DevOps, with IaC (Infrastructure as Code) becoming the de-facto standard for managing infrastructure (non-mainframe platform), horizontal scaling has become a built-in practice in deployment automations for production environments.
For distributed systems and cloud computing, managing increased (or decreased) traffic and load requires only an understanding of the automation mechanisms; no manual effort is involved in keeping an application working at the optimal level of performance.
Of course, with the multiple advantages horizontal PHP scaling provides, there are things to keep in mind before adopting it to the fullest. For instance, managing a distributed system with multiple machines can be more complex than managing a single machine. Ensuring data consistency can likewise prove challenging, though utilizing stateless architecture can help immensely.
Back to topPHP Scaling Tactic 4: Implement PHP Caching
PHP caching refers to the storage of frequently accessed data or content in a "cache," or temporary location. This practice provides faster response times, serving content significantly quicker than fetching it from a database or backend server. PHP caching also can reduce server load, save bandwidth during data transfers from the server to the client, and provide an improved user experience — all of which relate directly to performance and scalability.
Additionally, caching can be implemented at various layers of a PHP application architecture, as listed below:
- Client-Side Caching (Browser Caching) — Uses web browsers to store static assets (images, CSS, JavaScript) on the user's device, enabling faster loading on subsequent visits.
- Application-Level Caching — Stores data or objects in the memory of the application server, useful for user sessions, configuration settings, or business rules.
- Page-Level Caching — Stores complete HTML pages and serves them to users, suitable for websites with static or semi-static content.
- Fragment Caching — Caches specific parts of a web page that are frequently accessed or time-consuming to generate.
- Object Caching — Stores individual objects like user profiles or session data.
- Database Caching — Caches frequently executed database queries or frequently accessed data in the database server's memory or a separate cache service (Redis, Memcached, etc.).
- Content Delivery Network (CDN) Caching — CDNs store copies of web content at edge locations geographically closer to users, reducing latency and bandwidth consumption by serving content from the nearest server.
- Proxy Caching — Proxy servers act as intermediaries between the client and the origin server, storing copies of frequently accessed resources and serving them to users, reducing server load and improving response times.
How to Implement PHP Caching for Improved Scalability
Properly implementing caching in PHP platforms requires following a few steps and best practices, shown below:
- Identify Cacheable Data — Analyze data access patterns and identify frequently accessed or computationally expensive data that doesn't change too often.
- Choose Appropriate Caching Strategies and Types — Select the caching strategy and type (client-side, server-side, CDN, database, etc.) based on the specific needs of the application and the characteristics of the data being cached.
- Set Proper Cache Expiration Policies (TTL) — Define how long data should remain in the cache before it is considered stale and needs to be refreshed.
- Implement Cache Invalidation Mechanisms — Develop strategies to clear or update cached data when the underlying data changes, such as time-based expiration, event-driven invalidation, or versioning.
- Monitor Cache Performance — Regularly track key metrics like cache hit rate, cache miss rate, and latency to optimize caching efficiency and identify areas for improvement.
While implementing caching in your PHP platform, strive for a balance between serving fresh data, and only cache when necessary to prevent excessive memory usage and potential data staleness. Consider consistency between the cache and original data source, and be sure to encrypt sensitive data while implementing appropriate access controls to prevent unauthorized access.
Most of all, don't forget to plan for future PHP scaling needs. Utilize techniques like distributed caching, partitioning, and load balancing to handle high traffic and ensure application availability.
Back to topPHP Scaling Tactic 5: Establish a Proactive PHP Monitoring and Analysis Strategy
Proactive PHP monitoring involves actively observing and analyzing systems to identify and address potential problems before they disrupt operations or cause failures. It's a preventative approach that aims to maintain optimal performance and prevent issues from escalating, contrasting with reactive monitoring which responds to problems after they occur. This will simplify scaling PHP later, as issues are identified and mitigated before they can grow big, complicated, and deeply rooted in existing systems.
ZendHQ: Instant Application Insights
ZendHQ makes it easy for your team to monitor, manage, and optimize mission-critical PHP applications. Combined with ZendPHP runtimes, this extension smoothly integrates with existing PHP APMs (no re-platforming required), provides real-time root cause analysis, and more.
Key Aspects to PHP Monitoring and Analysis
The key aspects of proactive monitoring are the following:
- Early Detection — Identifying potential problems early on, before they become major issues
- Real-Time Analysis — Monitoring systems and applications in real-time detects anomalies and potential problems as they occur
- Predictive Capabilities — Using data analysis and machine learning to predict potential issues and take preventative measures
- Automated Alerts — Setting up automated alerts notify relevant teams when potential problems are detected, enabling quick responses
- Continuous Improvement — Regularly reviewing monitoring data and adjusting monitoring strategies ensures optimal performance and effectiveness
How Monitoring Benefits PHP Scalability
The benefits of proactive monitoring are many and very worth the time investment needed to build a comprehensive monitoring system. Reduced downtime or even zero downtime can be achieved by catching issues early, with the highest degree of debuggability if the monitoring system is properly implemented. Continuously improving performance is a major objective, accomplished through the identification and resolving performance bottlenecks; proactive monitoring ensures systems run efficiently.
For the end users, an enhanced experience is guaranteed because PHP monitoring can prevent issues that would negatively impact them, leading to increased satisfaction. Additionally, an indirect result of a correct monitoring approach is ‘cost savings,' as preventing problems before they escalate can save significant costs associated with downtime, repairs, and lost productivity. Finally, and immensely important, increased security can be achieved by addressing security vulnerabilities before they are exploited.
Back to topOn-Demand Webinar: How to Build a PHP Security Roadmap
Watch on your schedule as Principal Product Manager Matthew Weier O'Phinney explores how to go from reactive firefighting to proactive security management, including leveraging observability data for early threat assessment.
Final Thoughts
Scaling PHP is a strategic and required step for ensuring the long-term success and growth of your platform. By adopting a proactive approach to PHP platforms, organizations can ensure operational excellence, enhance user satisfaction, and maintain a competitive edge in today's dynamic business environment. However, effective PHP scaling requires a thoughtful approach, an adherence to best practices, and oftentimes advanced PHP knowledge. After all, scaling PHP is not a one-time effort, but an ongoing process.
The Zend team is here to help. Whether you're refactoring legacy code, adopting new systems, or fine-tuning your existing scalability approaches, we have the expertise needed to streamline your processes while minimizing expensive downtime. Check out our full suite of PHP services to learn more about how we can help you achieve your goals at scale.
Scale Enterprise PHP Applications with Confidence
The Zend Enterprise Web Platform simplifies automated scaling for mission-critical PHP applications through shared session state, asynchronous processing, and optimized resource management via a single unified command center. Learn more via the button below.
Additional Resources
- Guide - How to Develop Web Applications with PHP
- On-Demand Webinar - How to Scale Modern PHP Using ZendPHP + ZendHQ
- White Paper - The Costs of Building PHP In House
- Blog - PHP Maintenance and Tech Debt Trends
- Blog - PHP Web Application Hardening With CIS Hardened Docker Images
- Blog - Best Practices for PHP Log Analysis
