Blog
December 22, 2025
PHP Monitoring: Using PHP Observability Tools to Improve Web Apps
PHP Development
PHP monitoring is a crucial component for successful PHP web applications. A unified monitoring strategy, paired with well-chosen PHP observability tools, will let your team detect issues early, complete root-cause analysis, improve performance, and ensure a seamless user experience. This remains true whether you're managing a small-scale web app or a complex enterprise system.
In this blog, I cover the essentials of PHP monitoring and observability, including their key differences, how they work together, and their importance in maintaining application performance. You’ll also learn about tools, strategies, and best practices to monitor your PHP applications effectively.
PHP Monitoring and Observability Overview
Monitoring and observability are essential for keeping PHP applications healthy and performant. They provide the visibility needed to detect issues early, understand root causes, and optimize application behavior. Before we get into creating a PHP monitoring strategy, let's cover a few basics.
What Is PHP Monitoring?
PHP monitoring allows insight into application health by providing notifications when certain conditions occur, such as high CPU usage, high memory usage, slow requests, execution errors, and more.
You may either passively get details on events or issues by using the visualizations tools provided by a vendor, or you may setup the delivery of notifications to you actively on the channels of choice (SMS, email, Slack, ticket systems, etc.).
Learn More About Creating Custom PHP Alerts
PHP Monitoring vs. Observability
While PHP monitoring and PHP observability are often used interchangeably, there are a few differences between the two terms.
Where PHP monitoring is the process of collecting and analyzing predefined metrics to determine the health of your PHP app, PHP observability goes deeper. It provides context by combining logs, traces, and metrics to create a full picture of your current system. This makes it easier for teams to troubleshoot complex problems in distributed environments, such as PHP microservices or containerized PHP applications.
Generally speaking, PHP observability and PHP performance monitoring are used together to successfully manage critical PHP applications.
PHP Monitoring vs. Observability
| Aspect | PHP Monitoring | PHP Observability |
|---|---|---|
| Goal | Detect issues | Diagnose and understand issues |
| Data | Metrics only | Metrics, logs, and traces |
| Approach | Reactive; alerts after an issue has occurred | Proactive; prevents issues before they impact users |
| Use Case | Alerts for downtime or errors | Root cause analysis and optimization |
Why PHP Observability and Monitoring Matter
Every organization should have a well-implemented PHP monitoring and observability solution for their mission-critical PHP apps. This allows DevOps teams, and the organization as a whole, to resolve issues and PHP performance bottlenecks efficiently and reduce Mean Time To Resolution (MTTR).
This has a substantial impact on the bottom line of the business, as organizations do not have to deal with the unnecessary work involved in maintaining an extensive software analysis group.
Detect and Debug Issues Before They Become Problems
Related to the concept of MTTR, one of the most important features of a PHP monitoring system is the ability to detect and debug PHP issues, as close as possible to the initial development phase of the software development lifecycle (SDLC).
In order to do that, an enterprise-level PHP monitoring system must provide the capacity to drill down into call stack traces to diagnose performance bottlenecks, auto-discover business transactions, complete dynamic baselining, and run code-level diagnostics.
This will ensure a rapid issue identification and resolution, maintaining an ideal user experience for any mission-critical PHP application whether it runs on-premises or in the cloud.
PHP Monitoring and Performance Optimization
Often, faster troubleshooting isn’t enough. A great user experience is paramount for the success of a web application. Therefore, a valuable PHP monitoring system must guarantee a large set of data points, as intelligently aggregated as possible, related to areas of the execution that are not performing optimally.
Those areas include:
- Scope Analysis of Degradations - Which users are impacted by applications performance issues, for which transactions, when and how often?
- Fault Isolation - Identify the infrastructure layer responsible for the application performance degradation across network, endpoint, secured gateway, load balancers, front- and back-end servers) to direct the case to the right team for in-depth root cause analysis and performance management.
- Root Cause Analysis - Pinpoint the change, defect, or parameter which is creating the slow processing or errors.
Early Threat Detection Using PHP Performance Monitoring
As your PHP apps succeed and grow, your services scale in number and complexity. This makes it difficult to maintain a rapid pace of innovation while keeping your applications secure. It’s particularly challenging to respond to attacks, as DevOps and security teams need to collaborate to understand each attack’s root cause and remediate the vulnerabilities that enabled it.
It is critical to be able to identify risks from known PHP vulnerabilities in third-party libraries, PHP dependencies, and services, assuring that the only attack surface is limited to the proprietary logic developed in-house under the full control of DevOps and security teams.
A PHP app monitoring system can help teams to:
- Identify services/libraries exposed to security risks
- Understand those vulnerabilities
- See which elements have been exposed to attacks
- Mitigate active threats
On-Demand Webinar
How to Build a PHP Security Roadmap
In this on-demand webinar, Zend Principal Product Manager Matthew Weier O'Phinney goes through how to build a comprehensive PHP security roadmap, including discussions of using observability data to improve application security.
How to Choose the Right PHP Monitoring Tools
With so many PHP monitoring and observability tools available, it’s easy to feel overwhelmed and be unsure which option is the right choice for your applications. The key is to start by understanding your goals and evaluating tools based on how well they fit your PHP monitoring strategy.
Evaluating PHP Performance Monitoring Tools
When choosing PHP monitoring tools, always take the time to evaluate your goals and the tools at your disposal to ensure you’ve selected the best fit for your application and PHP monitoring strategy. It is important to emphasize some processes-related characteristics a PHP monitoring solution must unequivocally satisfy. These characteristics include:
- Easy to install in all components
- Easy to integrate in DevOps pipelines, bringing added value to such processes
- Enhancing the development experience
- High degree of configurability in order to tailor the various PHP APM features exactly to the needs of an application
- Easy visualization of actionable data
Pricing, PHP monitoring requirements, fitting into existing processes and observability tools, and how the PHP apps are deployed and consumed by the end users also impact which PHP monitoring solution is best for your applications.
Addressing Tool Sprawl in PHP Monitoring
As PHP applications grow in complexity, many teams adopt multiple PHP monitoring or observability tools to cover different needs, such as performance tracking, error logging, and infrastructure metrics. While this approach seems practical at first, it can quickly get out of hand and lead to tool sprawl.
This introduces several challenges to your PHP monitoring system:
- Data scattered across multiple dashboards makes it difficult to see the full picture, leading to fragmented insights
- Managing and maintaining several PHP monitoring tools increases workload for your team
- Paying for overlapping features across platforms quickly becomes very expensive
- Switching between tools to piece together root causes delays resolution, which can result in disrupted user experiences, increased downtime, and other consequences.
Many teams turn to Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) solutions to simplify monitoring and reduce complexity. While this approach can centralize some processes, it often introduces drawbacks such as limited flexibility, vendor lock-in, and reduced visibility into the underlying infrastructure.
Back to topHow to Monitor PHP Applications Effectively
Managing and monitoring multiple PHP applications in a complex system (which often is comprised of multiple databases, web servers, middleware, and more) has the potential to bury developer teams in complexity. As discussed above, each environment often comes with its own tools, dashboards, and alerts. This can leave operations fragmented and visibility limited. When critical issues arise, the lack of a unified monitoring solution can lead to slow detection, delayed responses, and rising costs.
That's why unified monitoring is no longer optional. In the modern ecosystem, it has become foundational.
By bringing PHP monitoring and observability under a single pane, enhancing it with deep PHP execution intelligence and metrics, businesses can shift from reactive monitoring to proactive control.
What Is the Zend Enterprise Web Platform?
The Zend Enterprise Web Platform is a unified command center that minimizes the work necessary to achieve comprehensive and unified PHP monitoring for critical applications. It delivers the simplicity of PaaS (secure runtimes, autoscaling, and advanced observability) without hidden costs, and gathers everything your team needs for effective PHP management onto one fully customizable dashboard. It reduces operational complexity and minimizes tool sprawl, all with zero operational overhead.
Check out this blog introducing the Enterprise Web Platform or watch this video to learn more:
In terms of design patterns, the platform comprises the following elements:
- Reverse Proxy Cache
- State Management (Stateful Server)
- Pub/Sub
- Asynchronous Job Processing Patters
- Log Aggregation
- Observability Design Patterns
Let's take a closer look at the last two items on that list. When using the platform, both log aggregation and observability design patterns have been configured according to best practices and coupled with a very simple "plug-and-play" modality for the ultimate user experience.
Log Aggregation
Logs aggregation is the practice of collecting, centralizing, and normalizing log data from diverse sources (such as servers, apps, or devices) into one place. This transforms scattered, raw data into structured and searchable insights for easier monitoring. It moves beyond simple collection to create actionable intelligence.
Observability Design Patterns
Observability design patterns are reusable solutions for understanding complex systems. They focus on extracting internal states via external outputs like logs, metrics, and traces. These are crucial for microservices and distributed systems to enable debugging, performance analysis, and proactive issue resolution by standardizing how data (what happened, how much, and how it flows) is collected, correlated, and analyzed across services.
Key patterns include log aggregation, distributed tracing, metrics collection, health check APIs, and exception tracking. Together, these patterns help developers ask arbitrary questions about their systems without prior knowledge of failures. They can also be used to achieve the following objectives:
- Debugging in distributed systems, making it possible to understand failures in complex, multi-service environments
- Performance tuning to help identify bottlenecks and inefficient code paths
- Proactive monitoring, enabling early detection of issues before they become major outages
- Data-driven decisions to allow you to ask and answer questions about system behavior without needing to redeploy or guess
How the Enterprise Web Platform Works
The Zend Enterprise Web Platform provides an Infrastructure as Code (IaC) architecture based on Kubernetes. It seamlessly sets up an infrastructure for PHP applications (in the form of a built image) that is already wired to convey all metrics and logs to an OpenSearch solution via an OpenTelemetry protocol.
The platform leverages OpenTracing protocol and userland libraries for application tracing, making it simple to reuse existing configurations within the proprietary code by pointing to the OpenSearch backend. Additionally, the system allows you to configure tags and other logging directives directly in the provided IAC with the combination of some environment variables. This enables the full segregation of logging and metrics per service and per application.
The entire underlying infrastructure, running services, and proprietary applications feed into OpenSearch, which acts as a single pane of glass and provides a unified monitoring experience. All observability data is available from a single, customizable dashboard, and your team can create visualizations to highlight the information that matters most for your applications and goals.
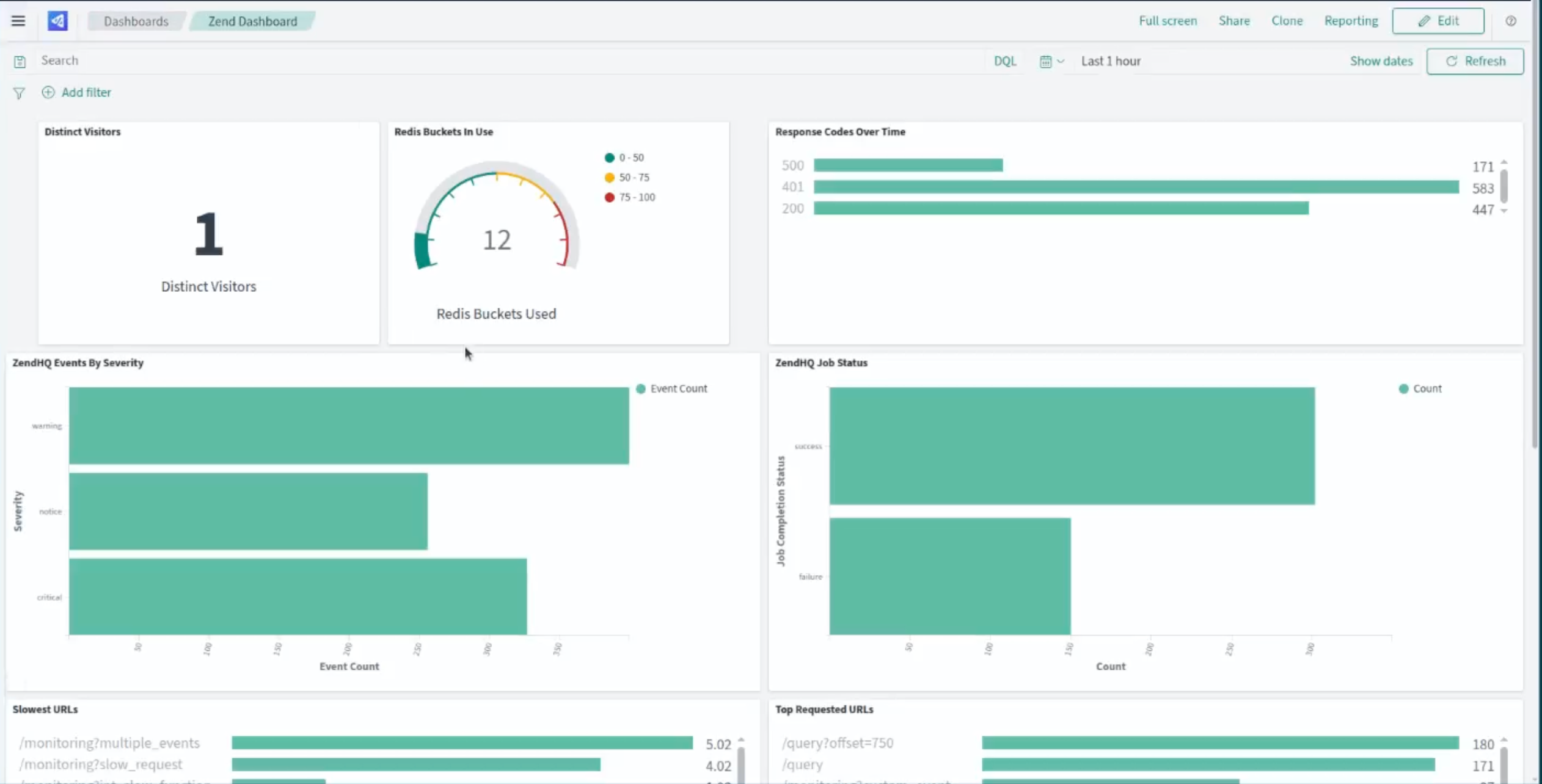
Default Metrics Patterns
While some metrics patterns will be implemented by default, the OpenSearch dashboard is designed for simplicity. You can easily add or customize graphical outputs generated by the indexed data. These are the metrics patterns included by default:
RED
Rate – requests/second
Errors – error count/rate
Duration – latency
USE
Utilization
Saturation
Errors
Blackbox Monitoring Pattern
Synthetic checks
Ping, HTTP GET, SSL expiry monitoring
SLA conformance monitoring
Other Metrics Patterns
You can also extrapolate the best value from other patterns. Here are a few examples:
Centralized Log Aggregation Pattern
Makes searching and correlating easy across microservices
Distributed Tracing Pattern
Span layering (frontend → web server → PHP app → DB)
Trace sampling (probabilistic or tail-based)
Baggage propagation (context through microservices)
Final Thoughts
The importance of PHP monitoring and observability tools cannot be overstated, and they should always be included in your web application security, management, and maintenance strategies. For teams looking to simplify PHP observability practices and reduce tool sprawl, the Enterprise Web Platform offers a unique solution. It delivers complete and unified monitoring, expert implementation services, ongoing support, and a security-first architecture. Take advantage of all the benefits of PaaS, but without expensive overhead or unexpected costs.
Secure, Scale, and Observe from a Single Source
The Enterprise Web Platform makes it easy to identify issues before they become expensive problems. Check out the walk through below, then contact Zend to schedule a free demo and see how it improves your infrastructure.
Additional Resources
- 101 Guide - PHP Security
- Blog - PHP Hardening: Strategies to Meet Compliance Requirements
- Blog - GDPR PHP Compliance: Maintaining GDPR for Web Applications
- Blog - Getting Started With Web Application Monitoring
- Blog - Choosing the Right PHP Stack
- Blog - Using PHP Performance Metrics for Early Threat Detection
