Blog
August 22, 2025
PHP remains one of the most widely used languages for building dynamic web applications, but is PHP secure? After all, its popularity also means that it is a a frequent target for cyberattacks. From SQL injection and cross-site scripting to misconfigured servers and outdated dependencies, security risks can emerge at every stage of your application's lifecycle.
However, to answer the question - yes, PHP is secure, which is part of what makes it such a strong choice for developing web applications. By following basic PHP security best practices, you can safeguard your applications against would-be attackers.
In this blog, I walk through a few examples of common risks and vulnerabilities that may get in the way of building more secure PHP. Next, I outline a few PHP security best practices to help you secure PHP applications against known and yet-to-be-disclosed vulnerabilities, recommending resources and services that can support your efforts.
How to Secure PHP: Common Threats and Vulnerabilities
PHP vulnerabilities are flaws that leave your applications open to possible PHP exploitation from malicious parties. If accessed, these vulnerabilities can be used to gain unauthorized access to your systems, leading to expensive fall out, damaged user trust, and other severe consequences. With new vulnerabilities discovered daily, and with PHP powering nearly 75% of web applications, working to effectively secure PHP becomes an ongoing process versus a one-and-done task.
The first step in reducing your application's attack surface and protecting user data is to understand common PHP vulnerabilities. Here are a few of the most prevalent PHP security issues that your team may face:
- Code Injection — A general term referring to attacks where injected code is interpreted and executed by applications, exploiting poor untrusted data handling and improper input/output data validation.
- Broken Access Control — Occurs when users are allowed to act outside their intended permissions, leading to unauthorized information disclosure, app modifications, destroyed data, or unauthorized business functions.
- Cryptographic Failures — Results from improperly protected sensitive data (passwords, credit card numbers, and other personal information) and is the root cause of sensitive data exposure.
- Session Hijacking — When malicious actors take control of a user's web session to steal or manipulate the session token, gaining unauthorized access to information and services.
These are just a few examples of threats to securing PHP applications and protecting your business from a costly data breach. However, by following a few PHP security best practices, you can make major strides in safeguarding your application, your users' data, and your business's reputation as a trustworthy and dependable partner.
Learn More About Identifying and Mitigating Common PHP Vulnerabilities
On-Demand Webinar
Take Mission-Critical Apps from At Risk to Locked Down
In this on-demand webinar, our expert walks through prevalent PHP vulnerabilities that could compromise your applications. They then take a deep-dive look into mitigation strategies to safeguard your PHP and mitigate risk.
7 PHP Security Best Practices
To create the most secure PHP websites and applications possible — and protect your and your customers’ sensitive data — start with these PHP security best practices. However, remember that this list is just the tip of the iceberg when it comes to securing PHP. Your team should be constantly evaluating emerging threats and your susceptibility to them, evolving your security strategies to match the current ecosystem.
1. Always Code With Secure PHP in Mind
As developers, we tend to use varying tools (e.g. SAST tools) that we don’t fully understand while under the stress of making a deadline where functionality takes precedence. The problem with this is that we end up introducing security flaws to our applications instead of creating PHP protection.
Frameworks and libraries have helped a lot with those concerns, and using the elements provided by those frameworks properly greatly reduces the risk of attacks. The obvious drawback is that frameworks themselves are sometimes vulnerable, and when a vulnerability is discovered in a framework, it affects the various applications written with it. To help you understand the tools you’re using, the OWASP Foundation releases an annual list of the top ten web app security risks and how to protect your applications against them.
Both the community and third-party sources (such as Zend) maintain lists of new and evolving CVEs, simplifying the process of keeping up with and mitigating emerging PHP security threats. Our Zend Security Center is designed to help developers identify and mitigate PHP vulnerabilities before they are exploited, keeping your PHP application secure and compliant.
Visit the Zend Security Center
2. Update All Application Components Regularly
PHP is constantly being improved upon, and with each new version comes added PHP protection and improvements for securing PHP applications. For this reason, it’s in your best interest to update to the latest version of PHP. Using an older version means you’ll stop receiving support over time — typically after four years — and you won’t be able to apply critical security patches and bug fixes to your application.
As mentioned earlier, code written within PHP is inherently vulnerable; there is always a door for a hacker with enough time, money, and resources to find their way in. This means your code must be as bulletproof as possible. With version updates come required changes to your code that add layers of protection and reduce the chance of an attack.
3. Understand and Document Your Existing Infrastructure
While this PHP security best practice may seem like a no-brainer, one of the biggest PHP security risks for large companies is that they don’t know the full extent of their IT infrastructure – which makes it almost impossible to keep that IT infrastructure patched and secure. Without adequate mapping, companies are likely deploying unpatched and/or end of life technologies, as discussed above.
This makes it important for companies to have a fully documented and regularly maintained software bill of materials that lists any technologies they deploy as part of their IT infrastructure. Maintaining this list makes it easy to quickly identify the components used in your applications, see the version they are running, and determine if they are vulnerable to new PHP CVEs, improving your PHP protection overall.
4. Deploy Hardened Container Images
Secure PHP starts with a solid foundation. One option for establishing that foundation is to leverage hardened PHP container images, such as those offered by Zend. Deploying these images will provide the pre-hardened and isolated environments required to meet recognized security benchmarks (such as those provided by CIS) while safeguarding applications against new and evolving threats.
Yet, despite the many benefits provided by utilizing containers, the 2025 PHP Landscape Report found that nearly 30% of PHP teams were not using container technologies and had no plans to do so in the future.
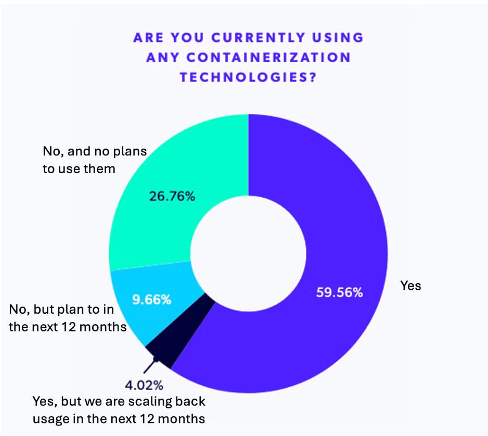
While many factors can play into a team’s decision not to deploy containers in their mission-critical applications — from upfront costs to managing a steep learning curve — the fact remains that these teams are leaving themselves more vulnerable to PHP exploitation and all the expenses that come with a successful web application attack.
Meet CIS Benchmarks With ZendPHP Hardened Docker Images
ZendPHP and ZendHQ Docker images are hardened to be compliant with CIS Docker Benchmarks v1.6.0. Use the buttons below to learn more or to access the Zend Container Registry.
5. Ensure Your PHP Infrastructure Is Properly Configured
Whatever patches and fixes you establish in your system won’t do much good if your infrastructure isn’t properly set up. Your infrastructure is likely made up of various tools, containers, load balancers, database servers, cache stores, and more. If they aren’t configured appropriately, if credentials are mismanaged, or if systems are not kept up to date, unauthorized users may gain access to restricted information. Data exchanged between the networks could be compromised, leading to less secure PHP.
Setting up your network also involves being aware of threats and setting firewalls and other protective measures to minimize the likelihood of them coming to fruition. Some of the risks involve:
- Unpatched security vulnerabilities
- Lack of a comprehensive credential management strategy
- Abuse of user account privileges
- Lack of encryption
6. Educate and Train All Employees in How to Maintain Secure PHP Apps
While total prevention is impossible, understanding how your systems work and their vulnerabilities will allow you to not only mitigate them, but respond to any attacks that do occur. Educate your team on common threats, as well as proper PHP development and deployment habits for securing PHP web applications — not just today, but in the long term.
Keeping data secure should be an organization-wide effort. After all, it’s not just technical attacks that can occur; social engineering can take place in various forms as well. Social engineering involves manipulation on the part of an attacker to gain access to confidential and sensitive information. Hackers may contact an employee outside of your IT department, via phone or email, to request access to certain internal materials by impersonating someone else. Through formal security training, you can educate all members of your staff on the appropriate actions to take in such situations, improving your PHP protection and security.
PHP Training
Expert-Led PHP Training: PHP Application Security
This in-depth, instructor-led course dives deep into how to secure PHP applications. Discover how to protect against common attacks, what goes into a security audit, cryptography basics, and much more.
Once teams are adequately trained in PHP security best practices, your business can ensure that secure PHP is a top priority. However, this is often much easier said than done. Development teams across the world are asked to balance the creation of new features and applications with PHP maintenance tasks, and many teams aren’t staffed to do both adequately.
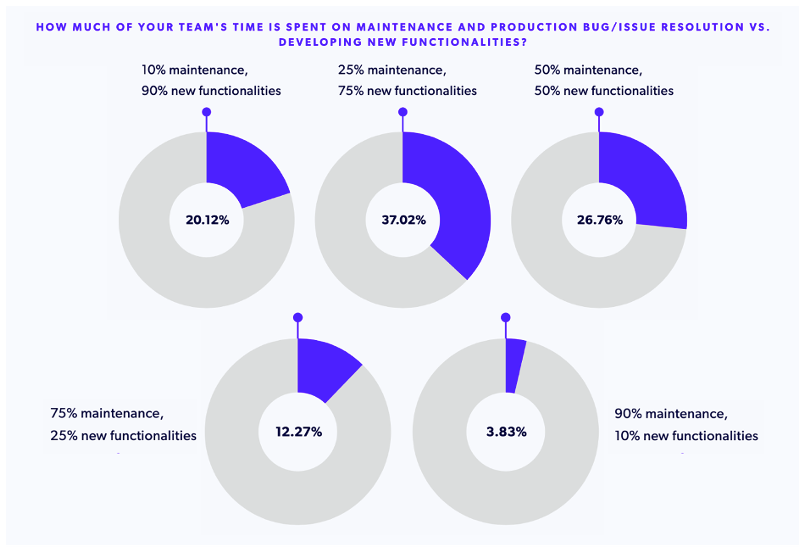
Based on the data we’ve seen in past PHP Landscape Reports, more teams are prioritizing new feature development over PHP application security, which means that – from a leadership perspective – securing PHP apps starts and ends with making sure your teams have the time needed to address your PHP security objectives.
7. Partner With Third-Party PHP Security Experts for Additional Support
Creating and maintaining secure PHP applications is an ongoing effort, one that requires time, buy-in, and continued prioritization within your organization. Without that, securing PHP applications will necessitate working with a third party, such as Zend. Here are a few ways that outside PHP security support can help your mission-critical applications:
- Ongoing security and bug fixes for EOL PHP through PHP Long Term Support (LTS)
- Custom PHP Consulting and Security Audits to diagnose issues in your current PHP security strategy
- Assistance planning and executing your next PHP Migration or Modernization project
By partnering with a trusted third party, you can simplify your path to more secure PHP without compromising on developing new features or reaching business goals.
Back to topFinal Thoughts
Securing PHP is not only a technical necessity, but a critical business imperative. Regular updates, proper configuration, employee training, and leveraging third-party expertise can all play a critical role in maintaining secure PHP applications. Whether you’re a developer, a team lead, or a business decision-maker, addressing security at every stage of development protects not only the safety of your applications but also the trust of your users. Stay proactive, stay informed, and continue to make secure PHP a priority at all stages of development.
Additionally, while this list of PHP security best practices is a good starting point, it is far from comprehensive. That’s where Zend can help. Whether you’re looking to fill knowledge or skill gaps within your team, or simply to free developers to focus on other tasks, we can help improve your PHP security and implement PHP security best practices throughout your applications.
Fortify Your PHP Applications Against the Latest Threats
The Zend Enterprise Web Platform delivers end-to-end protection with CIS-benchmarked images, continuous monitoring, and curated security alerts. Reduce your attack surface with a solution designed for mission-critical apps, all backed by the engineers who built the platform.
Discover the Enterprise Web Platform Additional Security Solutions
Additional Resources
- Guide - PHP Security
- Guide - How to Develop Web Applications with PHP
- On-Demand Webinar: Securing and Scaling PHP Applications
- Blog - PHP Dependency Management Using Composer
- Blog - GDPR PHP Compliance: Maintaining GDPR for Web Applications
- Blog - Fintech PHP Applications: How PHP Supports the Finance Sector
- Blog - PHP Observability and Monitoring Trends
- Blog - How to Build a Backup and Recovery Plan for PHP Web Apps
